15 + Corona Radiata Ct Scan Axial High Quality Images. The left corona radiata contains fibers which supply right leg and arm. In neuroanatomy, the corona radiata is a white matter sheet that continues ventrally as the internal capsule and dorsally as the centrum semiovale.

21 + Corona Radiata Ct Scan Axial High Quality Images
Doctors use CT scans to look at blood clots, tumors, bone fractures, and more.

A, CT chest scan showing the corona radiata sign in a ...

Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Axial, sagittal ...
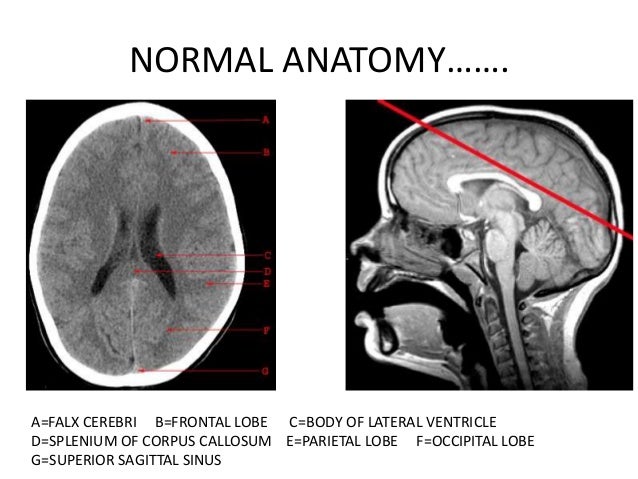
BASICS of CT Head

A, CT chest scan showing the corona radiata sign in a ...

Normal Anatomy | Radiology Key

CT scan of brain showing a 7mm diameter hypo density in ...

Thalamus and Basal Ganglia | Radiology Key
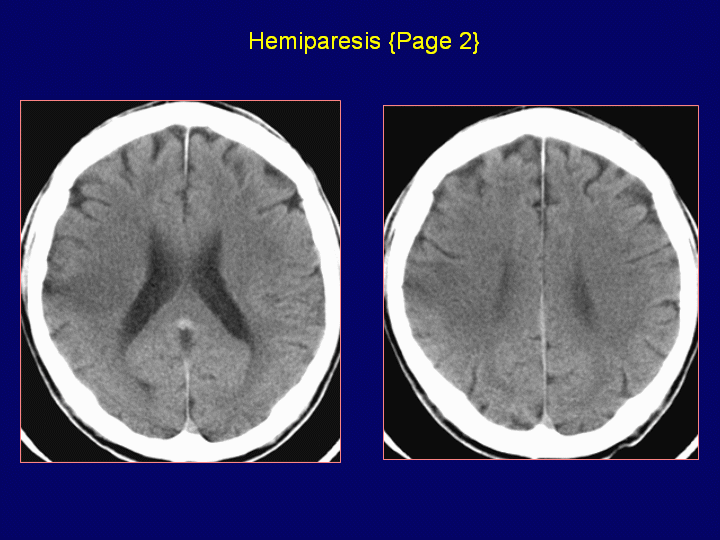
Case TF5-8

Head CT scan 27 h after thrombolysis shows hypodense le ...
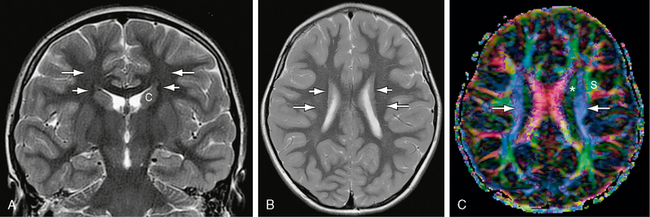
White Matter | Radiology Key
Internal capsule - wikidoc
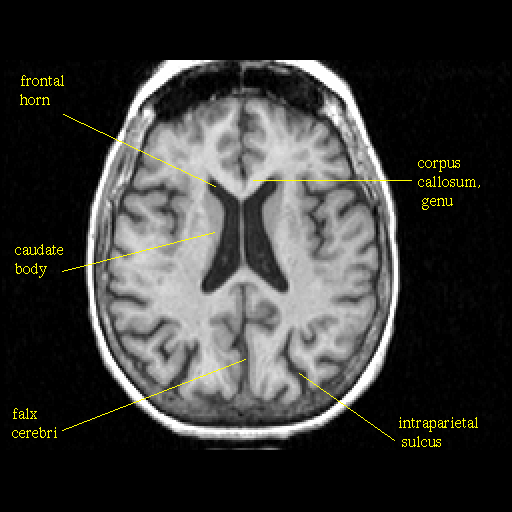
Table #11

Multicystic encephalomalacia | Eurorad
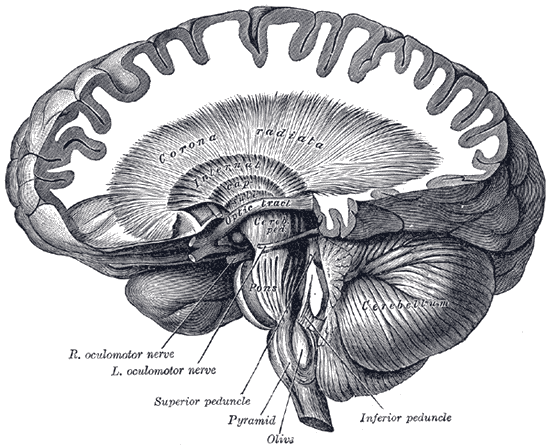
Corona radiata - Wikipedia

Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Identifies ...
15 + Corona Radiata Ct Scan Axial HD ResolutionsComputer axial tomography scan (CAT) of a head Doctor radiologist in hospital looking at mri x-ray scan of brain, head and skull ct scanning image on computer screen Baby head on ultrasound scan Head CAT Scan MRI Scan of head of human show head injury Magnetic resonance scan of the brain. Two different dataset has been tried. Proceeding downward from the cortex, the corona radiata becomes smaller and passes, in the form of a band, between the lenticular nucleus on the.

